IRS Notices & Letters: What to Do If You Get One
Receiving an IRS notice or letter can be stressful, but it doesn’t always mean you’re in trouble. Here’s how to understand, respond to, and resolve IRS correspondence effectively.
1. Why Did You Receive an IRS Notice?
The IRS sends notices for a variety of reasons, including: ✅ Balance due notifications (CP14, CP501, CP503).
✅ Refund adjustments (CP12).
✅ Underreported income or matching errors (CP2000).
✅ Audit or examination notices (Letter 2205-A, Letter 566).
🔗 Related: IRS Audit Triggers: How to Avoid an Unnecessary Audit
2. How to Read & Understand Your IRS Notice
🚨 Each notice has a letter or form number in the upper-right corner.
🚨 It explains why the IRS contacted you and what action is needed.
🚨 Some notices require a response, while others are just informational.
✅ Always verify the accuracy of the IRS claim before responding.
✅ Compare the notice to your tax return and financial records.
🔗 Related: New IRS Tax Law Changes for 2025
3. What to Do If You Disagree With an IRS Notice
✅ If the IRS made an error, you can dispute it by sending a written response with supporting documentation.
✅ For CP2000 (underreported income), you must reply by the due date or request additional time.
✅ If you need help, consider hiring a tax professional or calling the IRS directly.
🔗 Related: IRS Relief Programs: What Help Is Available for Taxpayers?
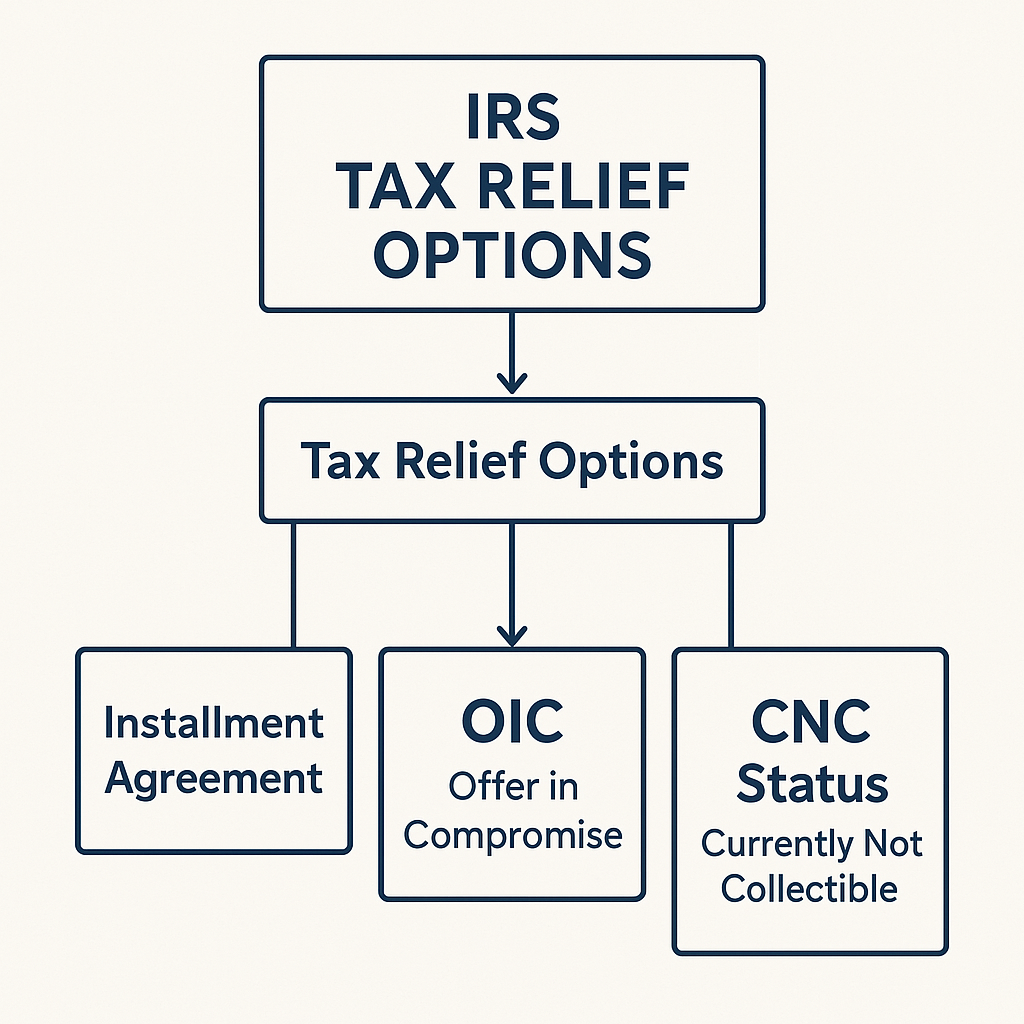
4. What to Do If You Owe Money
🚨 If you receive a balance due notice, pay as much as possible by the due date to avoid penalties.
🚨 If you can’t pay in full, apply for an IRS payment plan.
✅ Options include short-term and long-term installment agreements. ✅ Consider Offer in Compromise if you qualify for a tax settlement.
🔗 Related: How to Apply for an IRS Payment Plan
5. How to Contact the IRS About Your Notice
📌 Call the IRS phone number listed on the notice.
📌 Use the IRS Online Account to view your tax status.
📌 If you need more time, request an extension before the response deadline.
🔗 Related: Important IRS Deadlines & Filing Dates
Final Thoughts
An IRS notice doesn’t always mean bad news, but ignoring it can lead to bigger problems. Read your notice carefully, verify the information, and take action promptly.
🚀 Next Steps:
- Check your IRS notice type and required action.
- Dispute incorrect notices with documentation.
- Set up a payment plan if you owe taxes.
🔗 Need more IRS insights? Visit our IRS Tax Updates & Alerts Hub.